Send
Close Add comments:
(status displays here)
Got it! This site uses cookies. You consent to this by clicking on "Got it!" or by continuing to use this website.nbsp; Note: This appears on each machine/browser from which this site is accessed.
Installing the RIDES system
1. Installing the RIDES system
2. Course software
For the course, we need an editor and a compiler, both running under an operating system.
In class we use Cygwin for Windows, a Linux environment for Windows.
If you use dedicated Linux or Virtual machine Linux for Windows/Mac, please see me as there I have notes on the site, but not many students will take this option.
3. Overview
Here is a high-level overview.
Install and get Cygwin working. See Cygwin: Installation notes
Install Notepad++ if desired.
Login and download any class work such as A1, L1, etc., and extract to your Cygwin home directory (in the usual manner)
Do a one-time configuration of the ~/.bashrc file using Nano.
Verify that the changes have been made.
Details on these points are below.
4. Folder and file structure
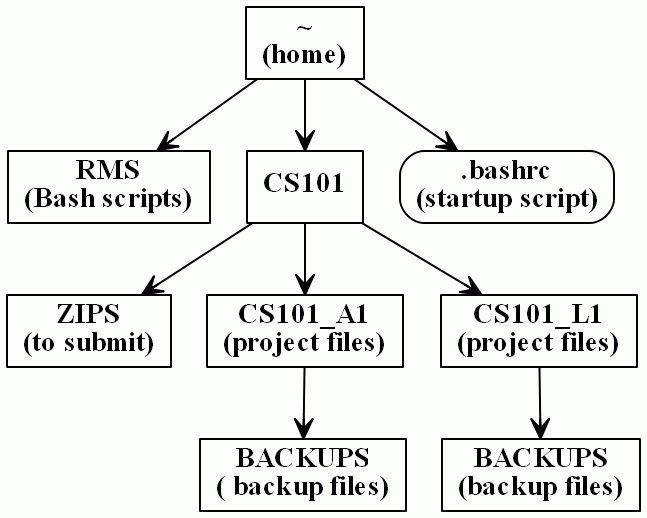
Here is a diagram of the general folder and file structure after downloading and extracting zip work files to the home directory.
5. Windows 10 customization
In Windows, select "
Start" in the lower left corner.
Notepad++ is a text editor for Windows. Find Notepad++ in start menu
Right click on Notepad++
Select "Pin to start"
Select submenu
Select "Pin to taskbar"
This will make it easier to start Notepad++.
Find Cygwin folder in start menu. Find Cygwin Terminal in the folder. Do the same thing as for Notepad++.
6. Operating systems
Linux is on operating system, like Windows.
Cygwin is a (pretend) Linux running on Windows.
7. Command line interface
Programmers should get to like the command line.
8. Shell programs
The command line is done via a shell program.
Linux uses the Bash shell, short for Bourne-Again Shell.
DOS command line (primitive)
PowerShell (very powerful)l
9. Files and folders
Linux: files and folders from the root /
Windows uses drive letters: C:, D:, E:, ...
10. Change directory
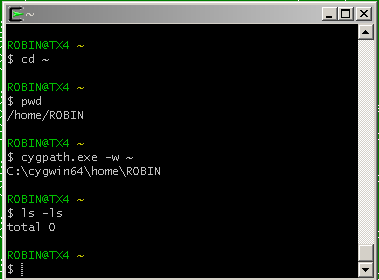
At the command line (two parts, separated by a space), type the following command and
Enter.
cd ~
The first part is cd (the command)
The second part is ~ (tilde, the option to the command)
This changes the current directory to the home directory.
11. pwd
At the Cygwin command line, type
pwd, for "
print working directory", and press
Enter.
pwd
The output should be something like the following.
/home/userid
This is your home directory/folder/subdirectory, with shortcut "
~" (tilde character).
12. Windows path
Type the following command and press enter.
cygpath.exe -w ~
This command is in three parts, with a space between each.
first part: cygpath.exe (the command)
second part: -w (the option for the command)
third part: ~ (the parameter for the option)
13. The RIDES system
The RIDES system is a collection of Bash script files to help in program development for an introductory programming course using Cygwin under Windows. The same scripts can work an a general Linux environment.
14. Folders
The following names are essentially the same on most operating systems.
folder
directory
subdirectory
15. Home directory
The home directory is where your user files are stored.
For user
ROBIN the absolute path is as follows.
/home/ROBIN
The shortcut is as follows (the tilde character "
~").
~
16. Windows Cygwin path
A useful command is the following, which displays the path to your home directory from Windows point of view.
cygpath.exe -w ~
On my system, the following is displayed.
D:\cygwin64\home\ROBIN
This path can be useful in finding your Cygwin files on a Windows system.
In the lab in KEC 119, the home directory is as follows, where
userid is your userid.
C:\cygwin64\home\userid
17. Executable files
Windows uses .exe for executable code files.
Cygwin uses that too.
Linux does not.
18. Installation
To install the system, the following needs to be done.
Download a zip file for a work requirement, such as A1, L1, etc.
Extract that zip file to your home directory. (See the Windows Cygwin path above)
This will update your work requirement files as well as the rms Bash scripts.
Note: Every work requirement has a
starter file and a work requirement file. The work requirement file is never overwritten, in case you need to download and extract the zip file again.
19. Zip files
A zip file is a compressed collection of folders and files.
Extract the zip file to the Cygwin home directory.
Copy-paste the path from the Cygwin window.
20. Cygwin
Go to Cygwin. type the command (two parts, separated by a space):
ls -ls
You should see the folders
RMS
CS101
RMS contains scripts to make programming in the course easier.
CS101 contains your work requirement folders.
21. One time configuration
The following is a one-time configuration. But, due to the way KEC 119 is set up, this configuration (and your project folders and files) are stored on the machine at which you are working. If you move to another machine, the files will not be there. Nor will the configuration. We will try to work out a way around this issue.
22. Using Nano
Nano:
Type the command nano ~/.bashrc.
Scroll to the bottom of the .bashrc file.
Add the following lines at the bottom of the
.bashrc file.
23. Lines to add
Add the following lines at the end of the file. If you prefer
nano, change
npp no
nano.
myEdit1=npp
myHome1=~
source ~/RMS/rmsInit.bsh
Note:
myHome1 has not yet been integrated into all of the scripts.
Do
not type a hash character "
#" before the line.
Save the file and exit. Close Cygwin and reopen it. To save the file in
nano, type
Ctrl-X,
y (for yes), and
Enter.
24. Notepad++
If you want to use Notepad++ on your own machine, you need to download and install it. See
Notepad++ .
By default, Notepad++ is installed to the following paths.
64 bit: C:\Program Files\Notepad++\notepad++.exe
32 bit: C:\Program Files (x86)\Notepad++\notepad++.exe
If you install it in some other place, then it will not work with the RIDES system, in which case you may need to start Notepad++ and manually open the desired code file.
25. Start Cygwin
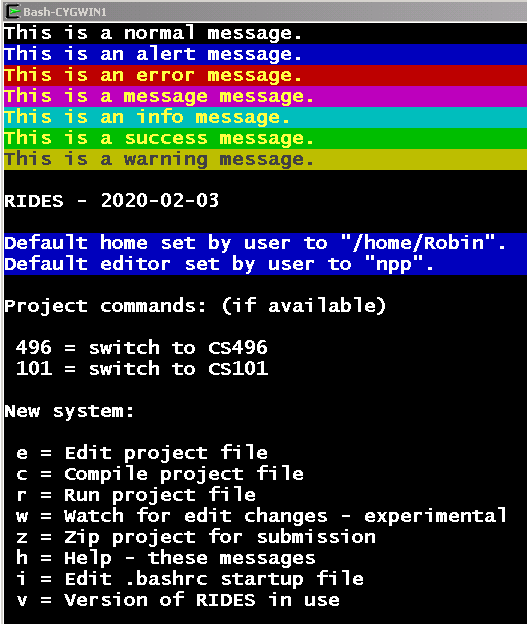
When you start Cygwin after installing the RIDES system, you should see something similar to the image. That is, some colored messages (normal, alert, error, message, info, success, warning), RIDES with version, Default home and editor (in blue), etc.
If not, you did not download a work and extract it properly, configure
.bashrc properly, etc.
26. Shortcut commands
Type
h (for help) and the available commands will be displayed. Note that the exact commands may change over time. Here is an example.
...
RIDES - 2020-02-03
Default home set by user to "/home/Robin".
Default editor set by user to "npp".
Project commands: (if available)
496 = switch to CS496
101 = switch to CS101
New system:
e = Edit project file
c = Compile project file
r = Run project file
w = Watch for edit changes - experimental
z = Zip project for submission
h = Help - these messages
i = Edit .bashrc startup file
v = Version of RIDES in use
Input edit:
i1 = input1.txt
i2 = input2.txt
... and so on ...
i9 = input9.txt
CS101 Assignments:
a1 = A1 : Name in big letters
a2 = A2 : Area of a trapezoid
... and so on ...
27. End of page
 Here is a diagram of the general folder and file structure after downloading and extracting zip work files to the home directory.
Here is a diagram of the general folder and file structure after downloading and extracting zip work files to the home directory.
 At the command line (two parts, separated by a space), type the following command and Enter.
At the command line (two parts, separated by a space), type the following command and Enter.
 When you start Cygwin after installing the RIDES system, you should see something similar to the image. That is, some colored messages (normal, alert, error, message, info, success, warning), RIDES with version, Default home and editor (in blue), etc.
When you start Cygwin after installing the RIDES system, you should see something similar to the image. That is, some colored messages (normal, alert, error, message, info, success, warning), RIDES with version, Default home and editor (in blue), etc.