Send
Close Add comments:
(status displays here)
Got it! This site uses cookies. You consent to this by clicking on "Got it!" or by continuing to use this website.nbsp; Note: This appears on each machine/browser from which this site is accessed.
Character data
1. Character data
2. Character data
A computer character is not the same thing as cartoon character.
A computer
character is a single letter, digit, etc., that is used to represent legible (i.e., readable) information. There are many different character sets.
7-bit standard ASCII character set (128 values)
8-bit extended ASCII character set (256 values)
16-bit Unicode character set (65536 values)
For a character set to be useful, everyone involved must agree on what the bit pattern for each character of a character set means.
A lot of data is either stored and/or sent as character data, or text. or can be thought of as being character data.
Standard email is transmitted as text.
Standard HTML web pages are text.
3. Character encodings
A
coding scheme assigns each character to a bit pattern.
EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code) is an older 9 bit character code, traditionally on IBM mainframe systems.
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is the character code on most personal computers.
standard ASCII - 7 bits (128 characters)
extended ASCII - 8 bits (256 characters)
4. ASCII
The standard ASCII character set (7 bit encoding) has
128 characters.
5. Extended ASCII
The extended ASCII character set (8 bit encoding) has
256 characters.
6. Standard codes
The standard ASCII code for "A" is 65d or 41h. Everyone agrees on that.
How does the character code for "A" appear? It depends on the context (font, size, color, etc.).
7. The letter A
8. Bit encoding


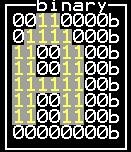

In a bit-mapped font, bits that are
0 or
1 can be made to look like letters by appropriate display techniques.
Note: A vector font is handled differently than a bit-mapped font.
9. Unicode
Unicode is a 16-bit character code that handles additional characters as found, for example, in Chinese and Japanese.
The Unicode character set has
16 bits in order to represent
65536 characters.
The first
127 characters are the same as the standard ASCII character set.
More information is available at
http://www.unicode.org [as of 1, 11 17, 2003].
10. Hebrew
Languages such as Arabic and Hebrew go from right to left.
By contrast, English goes from left to right.
11. Decimal form
Here is the decimal form (for HTML usage).
אבגדהוזחט
יךכלםמןנס
עףפץצקרשת
Here is how it appears when formatted (as HTML).
אבגדהוזחט
יךכלםמןנס
עףפץצקרשת
Note that each language uses part of the 65,536 Unicode character space. The ASCII character set uses the first 256 character slots.
12. Hexadecimal form
Here is the hexadecimal form (for HTML usage).
אבגדהוזחט
יךכלםמןנס
עףפץצקרשת
Here is how it appears when formatted (as HTML).
אבגדהוזחט
יךכלםמןנס
עףפץצקרשת
13. ASCII
Here is how it appears in ASCII when typed from a console window.

Notice the strange characters. That is because a 16-bit Unicode character set is being typed in a Window that is expecting 8-bit ASCII characters.
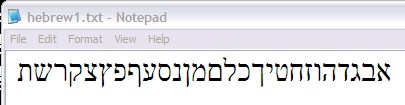
14. Notepad
Here is how the above text looks in Notepad that, by default, will use a 16-bit Unicode character set.
15. BabelMap
BabelMap is a Windows character map utility that allows you to find and copy any Unicode character. ... It is free and fully functional, and there are no disabled features or time restrictions. ... Whilst BabelMap is free, if you do use it for commercial purposes, please consider making a small donation by means of PayPal to help support its continued development. http://www.babelstone.co.uk/software/babelmap.html [as of 1, 3 14, 2005]
16. End of page
17. Multiple choice questions for this page
9 questions omitted (login required)
18. Acronyms and/or initialisms for this page
2 acronyms omitted (login required)


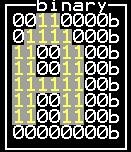
 In a bit-mapped font, bits that are 0 or 1 can be made to look like letters by appropriate display techniques.
In a bit-mapped font, bits that are 0 or 1 can be made to look like letters by appropriate display techniques.
